Basic Concepts
The split normal distribution (aka the two-piece normal distribution) splices two normal distributions with the same mode but possibly different variances together at the mode.
The probability density function (pdf) of this distribution, denoted N(μ, σ12, σ22), is
An alternative expression for the pdf is
where φ(z) = the pdf of the standard normal distribution at z. Using Excel, we see that φ(z) = NORM.S.DIST(z,FALSE) and φ((x-μ)/σ) = NORM.DIST(x, μ, σ, FALSE).
The cumulative distribution function (cdf) is
where Φ(z) = the cdf of the standard normal distribution at z. Using Excel, we see that Φ(z) = NORM.S.DIST(z,TRUE) and Φ((x-μ)/σ) = NORM.DIST(x, μ, σ, TRUE).
The inverse of the cdf is
where σ = (σ1+σ2)/2.
Properties
Key properties of the split normal distribution are
Worksheet Functions
Real Statistics Functions: The Real Statistics Resource Pack provides the following functions.
SNORM_DIST(x, μ, σ1, σ2, cum) = the probability density function value f(x) for the split normal distribution when cum = FALSE and the corresponding cumulative distribution function F(x) when cum = TRUE.
SNORM_INV(p, μ, σ1, σ2) = the value x such that SNORM_DIST(x, μ, σ1, σ2, TRUE) = p, i.e. inverse of SNORM_DIST(x, μ, σ1, σ2, TRUE).
References
Julio, J. M. (2007) The fan chart: the technical details of the new implementation
https://www.banrep.gov.co/docum/ftp/borra468.pdf
Wikipedia (2022) Split normal distribution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Split_normal_distribution
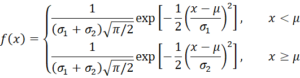
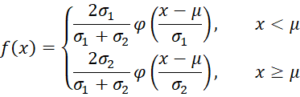
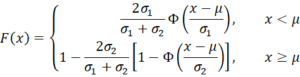
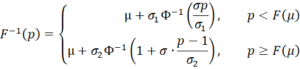
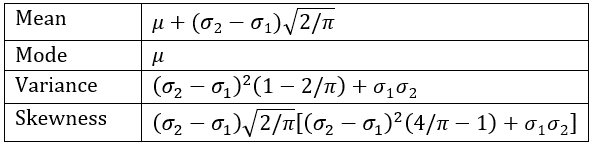
Where can I find an EXCEL example of a Split normal distribution?
Ron,
What sort of example are you looking for?
Charles