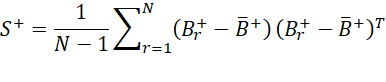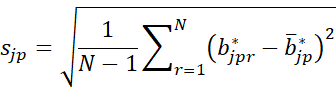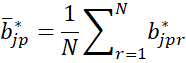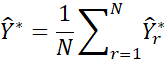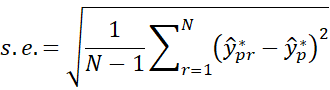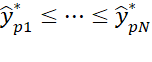Objective
Our objective is to show how to use bootstrapping in multivariate regression modelling. In particular, we describe how to estimate standard errors and confidence intervals for regression coefficients, and prediction intervals for modeled data. Bootstrapping is especially useful when the normality and/or homogeneity of variance assumptions are violated. This webpage extends the concepts described in Bootstrapping for Regression to multivariate regression.
See the following links for further information about bootstrapping:
Click here for a description of Excel worksheet functions provided by the Real Statistics Resource Pack in support of bootstrapping for multivariate regression models. Eamples are also provided.
Bootstrapping for regression coefficient covariance matrix
We provide two approaches for calculating the covariance matrix of the regression coefficients.
Approach 1 (resampling residuals)
We assume that X is fixed. Using the original X, Y data, estimate the regression coefficients via
B = (XTX)-1XTY
Next calculate
E = Y – XB
We now create N bootstrap iterations. For each iteration, create an E* by randomly selecting n rows from E with replacement. Next calculate
Y* = XB + E*
and use regression to calculate the regression coefficients B* based on the data in X, Y*; i.e.
B* = (XTX)-1XTY*
and use regression to calculate the regression coefficients B* based on the data in X, Y*. For each B* define B+ where B+ is a km x 1 column array consisting of the columns in B* stacked one on another.
We now have N bootstrap matrices B1+, …, BN+. Now calculate the average of each of these matrices and then calculate the km × km bootstrap covariance matrix
Finally, we unstack the km × 1 main diagonal D+ of this matrix to obtain the k × m matrix of bootstrap variances D* of B. The square roots of the values in D* serve as the standard errors of the regression coefficients in B.
Approach 2 (resampling cases)
This time we create N bootstrap iterations as follows. For each iteration, randomly select n random numbers from the set 1, …, n. We now define X* and Y* as follows. For each such random number i assign the ith row of X to the next row in X* and the ith row of Y to the next row in Y*. For this X*, Y*, perform regression to estimate the regression coefficient matrix B*. Now calculate B+, S*, S+, D+, D* as described above.
Bootstrapping regression coefficient confidence intervals
We can use the same two approaches to create confidence intervals for the individual regression coefficients. Using either approach, calculate the N bootstrap k × 1 coefficient matrices B*1, …, B*N where each B*r is a k × m coefficient matrix. The bootstrap standard error for each element βjp in β can be estimated by
where
We can also calculate a 1 – α confidence interval for each βjp by first arranging the jpth coefficient for each bootstrap coefficient matrix in order
The 1 – α confidence interval is then
Bootstrapping confidence intervals for data
The standard error and confidence interval for Ŷ = X0β where X0 is a 1 × k+1 row vector (with initial element 1), is produced by first generating N bootstrap values B*1, …, B*N for the coefficient matrix as described above. For each B*r we calculate the predicted Y value for X0, namely
Finally, the bootstrap prediction is
The standard error for each ŷp is then
Arranging the N bootstrapped predicted yp values in order
we obtain a 1 – α confidence interval for each ŷp as follows
Bootstrapping prediction intervals for data
Our goal is to find bounds for Y = X0β + ε. There are two sources of uncertainty: estimate of β by B, and the uncertainty of ε. We use the same as for the confidence interval, except that we need to add uncertainty for ε.
If the homogeneity of variances assumption is met, then for each bootstrap B*r we can select one of the n entries in E*rp at random (call it e*rp) and use it to serve as the bootstrap version of εp. Here E*rp = Y*rp – B*rpX when using Approach 1 and E*rp = Y*rp – B*rpX*rp when using Approach 2.
For each column p, we obtain the needed estimate
Arranging these in increasing order, we obtain the 1-α prediction interval for each p.
Modification
Instead of using the ordinary residuals, we could use mean-centered variance-adjusted residuals as described in Bootstrapping for Regression.
References
Eck, D. J. (2017) Bootstrapping for multivariate linear regression models
https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.07040
Stine, R. A. (1985) Bootstrap prediction intervals for regression
https://www.jstor.org/stable/2288570?seq=1
Fox, J. (2015) Bootstrapping regression models.
Applied Regression Analysis and Generalized Linear Models, 3rd ed. Sage Publishing
https://us.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-binaries/21122_Chapter_21.pdf
Stack Exchange (2021) Bootstrap prediction interval
https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/226565/bootstrap-prediction-interval
Roustant, O. (2017) Bootstrap & confidence/prediction intervals
https://olivier-roustant.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/bootstrap_conf_and_pred_intervals.pdf