Basic Concepts
Generally to understand some characteristic of the general population we take a random sample and study the corresponding property for the sample. We then determine whether any conclusions reached about the sample are representative of the population.
This is done by choosing an estimator function for the characteristic (of the population) that we want to study and then applying this function to the sample to obtain an estimate. By using the appropriate statistical test we then determine whether this estimate is based solely on chance.
The hypothesis that the estimate is based solely on chance is called the null hypothesis. Thus, the null hypothesis is valid if the observed data (in the sample) do not differ from what would be expected based on chance alone. The complement of the null hypothesis is called the alternative hypothesis.
The null hypothesis is typically abbreviated as H0 and the alternative hypothesis as H1. Since the two are complementary (i.e. H0 is true if and only if H1 is false), it is sufficient to define the null hypothesis.
Caution
Since the sample usually only contains a subset of the data in the population, we cannot be certain as to whether the null hypothesis is true or not. We can merely gather information (via statistical tests) to determine whether it is likely or not. We therefore speak about rejecting or not rejecting (aka retaining) the null hypothesis based on some test, but not accepting the null hypothesis or the alternative hypothesis. Often in an experiment, we are actually determining the validity of the alternative hypothesis by testing whether or not to reject the null hypothesis.
Types of Error
When performing such tests, there is some chance that we will reach the wrong conclusion. In fact, here are two types of such errors:
- Type I – H0 is rejected even though it is true (false positive)
- Type II – H0 is not rejected even though it is false (false negative)
The acceptable level of Type I error is designated by alpha (α), while the acceptable level of Type II error is designated beta (β).
Significance
We use the following terminology:
Significance level is the acceptable level of type I error, denoted α. Typically, a significance level of α = .05 is used (although sometimes other levels such as α = .01 may be employed). In other words, we are willing to accept the fact that in 1 out of every 20 samples we reject the null hypothesis even though it is valid.
P-value (the probability value) is the value p of the statistic used to test the null hypothesis. If p < α then we reject the null hypothesis.
Critical region is the part of the sample space that corresponds to the rejection of the null hypothesis, i.e. the set of possible values of the test statistic that are better explained by the alternative hypothesis. The significance level is the probability that the test statistic will fall within the critical region when the null hypothesis is assumed to be true.
Usually, the critical region is depicted as a region under a curve for continuous distributions (or a portion of a bar chart for discrete distributions).
The typical approach for testing a null hypothesis is to select a statistic based on a sample of fixed size, calculate the value of the statistic for the sample, and then reject the null hypothesis if and only if the statistic falls in the critical region.
One-tailed tests
One-tailed hypothesis testing specifies the direction of the statistical test. For example, to test whether cloud seeding increases the average annual rainfall in an area that usually has an average annual rainfall of 20 cm, we define the null and alternative hypotheses as follows, where μ represents the average rainfall after cloud seeding.
H0: µ ≤ 20 (i.e. average rainfall does not increase after cloud seeding)
H1: µ > 20 (i.e. average rainfall increases after cloud seeding
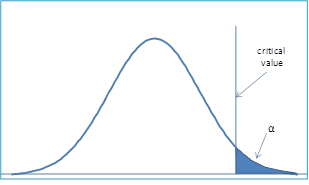
Here the experimenters are quite sure that the cloud seeding will not significantly reduce rainfall, and so a one-tailed test is used where the critical region is the shaded area in Figure 1. The null hypothesis is rejected only if the test statistic falls in the critical region, i.e. the test statistic has a value greater than the critical value.
Figure 1 – Critical region is the right tail
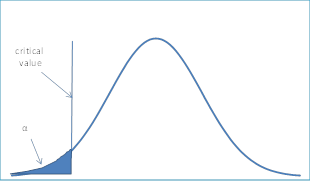
The critical value region here is the right (or upper) tail. It is quite possible to have one-sided tests where the critical region is the left (or lower) tail. For example, suppose the cloud seeding is expected to decrease rainfall. Then the null hypothesis would be as follows:
H0: µ ≥ 20 (i.e. average rainfall does not decrease after cloud seeding)
H1: µ < 20 (i.e. average rain decreases after cloud seeding)
Figure 2 – Critical region is the left tail
Two-tailed tests
Two-tailed hypothesis testing doesn’t specify the direction of the test. For the cloud seeding example, it is more common to use a two-tailed test. Here the null and alternative hypotheses are as follows.
H0: µ = 20
H1: µ ≠ 20
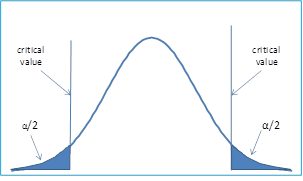
The reason for using a two-tailed test is that even though the experimenters expect cloud seeding to increase rainfall, it is possible that the reverse occurs and, in fact, a significant decrease in rainfall results. To take care of this possibility, a two-tailed test is used with the critical region consisting of both the upper and lower tails.
Figure 3 – Two-tailed hypothesis testing
In this case, we reject the null hypothesis if the test statistic falls on either side of the critical region. To achieve a significance level of α, the critical region in each tail must have size α/2.
Statistical power
Statistical power is 1 – β. Thus power is the probability that you find an effect when one exists, i.e. the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis. While a significance level for type I error of α = .05 is typically used, generally the target for β is .20 or .10, and so .80 or .90 is used as the target value for power.
Testing procedure
The general procedure for testing the null hypothesis is as follows:
- State the null and alternative hypotheses
- Specify α and the sample size
- Select an appropriate statistical test
- Collect data (note that the previous steps should be done before collecting data)
- Compute the test statistic based on the sample data
- Determine the p-value associated with the statistic
- Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis by comparing the p-value to α (i.e. reject the null hypothesis if p < α)
- Report your results, including effect sizes and confidence intervals
Caution
Suppose you perform a statistical test of the null hypothesis with α = .05 and obtain a p-value of p = .04, thereby rejecting the null hypothesis. This does not mean there is a 4% probability of the null hypothesis being true, i.e. P(H0) =.04. What you have shown instead is that assuming the null hypothesis is true, the conditional probability that the sample data exhibits the obtained test statistic is 0.04; i.e. P(D|H0) =.04 where D = the event that the sample data exhibits the observed test statistic.
References
Howell, D. C. (2010) Statistical methods for psychology, 7th Ed. Wadsworth. Cengage Learning
https://labs.la.utexas.edu/gilden/files/2016/05/Statistics-Text.pdf
Zar. J. H. (2010) Biostatistical analysis 5th Ed. Pearson
Hi Charles,
I have a query. I’m conducting a market research wherein i have 4 factors, say A,B,C and D affecting one thing, for example, say factors contributing to brand loyalty.
Now, for A,B,C & D, i have 70 responses wherein the users have given a ‘1’ or a ‘0’, a 1 indicating that particular factor matters and 0 meaning it doesnt matter. (I have 70 rows of 4 columns of 1s and 0s in excel)
Now, i want to find which factors( out of A,B,C,D) are relevant for brand loyalty using hypothesis testing.
Which tests should i do? ( chi-square, 1 way anova or any other tool on excel?)
My current hypothesis is : Factors A,B,C,D are significant for brand loyalty. Does it need to be changed?
Please provide some insights.
Kabeer,
I don’t know of any absolute criteria for brand loyalty, and so I don’t know of any test which will determine which factors are significant for brand loyalty. You can test whether there are significant differences between the ratings of the four factors or correlations between the factors, but these don’t determine whether a particular factor is significant. You can, of course, set your own criteria (e.g. at least x% of the raters find a particular factor important), especially if you have earlier studies to support your criteria.
Charles
Hi
My question is the original claim is that the mean amount of organic matter in soil is 3%. the competing claim is that the mean amount of organic matter in soil is something other than 3%.
State the null hypothesis, H0, in symbolic form: I wrote u=0.03
State the alternative hypothesis, H1, in symbolic form: I wrote u<0.03
Am I right for both answers? *u is pronounce mu for sample mean*
Thanks
Katrina
Katrina,
This is correct in the one-tailed test. For the two-tailed test, the alternative hypothesis is u not equal to .03.
Charles
both are correct of my answers are correct? Or last one is u not equal to .03?
Thanks
Katrina
Hi Charlse,
I have a question, what is the null and alternative hypothesis from reading this study case:
According to theory, different positions occupied by personnel in an organisation strongly inform their levels of
job satisfaction. Job satisfaction refers to the persons feelings towards their work, and is intimately tied-up
with their motivation towards getting their work done. It is defined as “the pleasurable emotional state
resulting from the appraisal of one’s job as achieving or the achievement of one’s job values”. Job satisfaction
is determined by factors such as job design, responsibility, level of difficulty, recognition, ability to progress,
task identity and so forth. These factors are all part of the position held by an employee in an organisation.
Considering the above, you are the HR manager at a company, and wish to determine if some employees
occupying certain positions experience more job satisfaction than others. You administer a questionnaire to all
employees at your company and develop an overall score measuring job satisfaction.
You record the employee’s position as:
General Worker
Junior Management
Middle Management
Senior Management
You develop an aggregate score for Job Satisfaction. You sample 50 employees
You should be able to state the null and alternative hypotheses based on “considering the above, you are the HR manager at a company, and wish to determine if some employees occupying certain positions experience more job satisfaction than others”.
Charles
hello can you help me to make hypothesis and identify null and alternative hypothesis by using SPSS
I don’t use SPSS, but the concepts of null and alternative hypotheses are the same in SPSS as those described on this webpage.
Charles
Suppose a chemical company has developed a catalyst that is meant to reduce reaction time in a chemical process. For a certain chemical process, reaction time is known to be 150 seconds. The researchers conducted an experiment with the catalyst 40 times and measured reaction time. The researchers reported that the catalysts reduced reaction time with a P-value of 0.02.
1) Identify the null and alternative hypotheses.
2) Explain what this result means. Do you believe that the catalyst is effective? Justify and explain your reasoning.
I need extreme help with this problem
Anthony,
1) Probably the null hypothesis is that the catalyst does not reduce reaction time and the alternative hypothesis is that it does
2) If alpha = .05, then p-value = .2, means that you have a significant result (which supports the alternative hypothesis that the catalyst is effective).
Charles
what is null hypothesis
Muhammad,
Sorry, but I don’t understand your question. The null hypothesis is whatever you want it to be as described on the referenced webpage.
Charles
I’m sorry, the text was incomplete.
Three variables: a, b, and c.
H0: R(a,c)-R(b,c) = 0
H1: R(a,c)-R(b,c) > 0
My question is: I heard that you should not put inequality signs in H0, because you need to test a defined parameter. You should put inequality signs only in H1. But then, what to do with the cases where R(a,c)-R(b,c) < 0?
These are naturally included in H0, right? Because H1 only admits positive values, hence everything else is part of H0. Is this correct?
Thanks,
Miguel
Dear Charles,
I’m sorry, parts of my previous messages didn’t appear on the post (too much text?)
My hypothesis is:
H0: R(a)-R(b) = 0
H1: R(a)-R(b) > 0
Perhaps with this aditional info we can understand my question. Otherwise I’ll post it again.
Many thanks,
Miguel
Miguel,
I don’t understand what R(a) means. The correlation coefficient is R(a,b). Do you mean H0: R(a,b) = 0 vs. H1: R(a,b) not = 0.
Charles
Dear Charles,
As I understand it, the null hypothesis (H0) should never be stated with an inequality sign (), but always with an equal sign (=), due to the fact that there needs to exist a defined parameter to be tested for likelihood.
In the case of the one-tailed hypotheses, you wrote:
H0: µ ≥ 20 (i.e. average rainfall does not decrease after cloud seeding)
H1: µ 0
In which R(a) is one correlation coefficient and R(b) another one, of the variables a and b against a common variable c. Now, I am able to reject the null hypothesis in almost every case, but there are some cases where R(a)-R(b)=0 (so H0 is not rejected), but also some other cases where R(a)-R(b)<0. Now, my question is:
Are both results [R(a)-R(b)=0 and R(a)-R(b)<0] equal motives for H0 rejection? In other words, should I treat R(a)-R(b)<0 as a rejection of H0, or differently?
Best regards,
Miguel Serra
Porto, Portugal
Miguel,
I don’t understand why you are referring to correlation coefficients R(a) and R(b). These are not relevant to the problem at hand. In any case, it is probably better to look some specific examples, such as the following:
Example 1 of https://real-statistics.com/sampling-distributions/one-sample-hypothesis-testing-central-limit-theorem/
Charles
I have trouble finding the critical value and the TV in every problem. I’m hoping you could help me…
For example, One hundred people were placed on a special exercise program. After one month, 61 lost weight, 11 gained and 28 weighed the same as before. Test the hypothesis that the exercise program is effective at alpha=0.02 (Note: It will be effective of fewer than 50% of the people did not lose weight.)
Jocelyn,
For this problem, you need to decide which test to use to test the null hypothesis that at least 50% of the people lost weight. Hint: Possible choices are the binomial test or one-sample t test.
Charles
Charles
I have a question and hope you could help me. I have a null hypothesis as ‘there is a negative effect of X on Y’ and an alternative hypothesis as ‘there is a positive effect of X on Y’. P-value is set at .05.
I use linear regression for the test and find that the unstandardized coefficient between X and Y is -.503 and Sig is .828. In this case, I should reject or accept the null hypothesis and why?
Thanks for you help.
Since sig = .828 > .05 = alpha, you would retain the null hypothesis. Note that you don’t “accept” the null hypothesis, but merely state that you don’t have sufficient reasons to reject it. This null hypothesis is that the corresponding regression coefficient is zero.
Whether this null hypothesis is the same as your null hypothesis is not completely clear to me without further information.
Charles
How do you state a null hypothesis saying the effect of beta will be greater than 100.000?
Astrid,
What is beta? Clearly you aren’t referring to the type II error since that can’t exceed 100%.
Charles
Is IT possible to test alternative hypothesis as 5*beta >25000 ?
The point is to test if an increase of 5 in the beta variable is larger than 25000
Sorry Anette, but I don-t understand your question.
Charles
Should we use alternative or null hypotheses with t-test analysis???
The test is for the null hypothesis, although since the alternative hypothesis is the complement of the null hypothesis it can also be viewed as a test for the alternative hypothesis.
Charles
Finally, I think to grasp the NHST behaviour in simple terms.
The Null Hypothesis, H0: p=p0 should be thought has an
approximate condition The same thing for the Alternative H1: p=p1
Note that the latter value p1 is called strictly in order to calculate the Type II error. In fact. it is absolutely absent at the test formula which is deduced supposing the Null true.
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle: Once you eliminate the impossible whatever remains, no matter how improbable, must be the truth.
I modify slightly
Once I eliminate the unlike, what remains has good chances to be plausible.
(impossible to go further).
please i need examples of null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis as many as possible
Okunola,
You can see these throughout the website.
Charles
Hello Sir. Do you know the answer to this?
” If you had a free hand, explain how you would like to conduct an appropriate hypothesis test and explain why your method is better. ”
This sounds like a homework assignment. I prefer not to answer such questions, although some ideas can be found on the referenced webpage.
Charles
Respected sir,
Would you please like to share some real life examples of a (alpha) in terms of average?
Ghulam Ishaq
Student of Business Administration
The University of Poonch.
AJ&K,Pakistan
Usually alpha is set to .05.
Charles
Dear Sir, I have read somewhere that one can only test NULL hypothesis and one cannot test ALTERNATIVE hypothesis ……..Is it true? Why so ?
Dave,
The tests are all set up to test the null hypothesis, but keep in mind that the alternative hypothesis is true if and only if the null hypothesis is false.
Also when you calculate the the power of a test, in some sense you are testing the alternative hypothesis.
Charles
Charles
“Acceptance Interval”, indeed?
There are lots of people that uses this designation
I do prefer to name it “No-rejection”
What do you think about?
Luís
Charles, please
Would, you so kind to cut after “Well done Charles” changing (April 6, 23:30)
confusing/incorrect text by the following:
Though we deliberated to retain 95% (say) probability to the Null Hypothesis
and a scarce 5% to the Alternative we are never apt to “accept” H0, not whithstand
found in a no few statistical literature. Jargon? could be, but dangerous
for beginners. On contrary In case the test falls outside ill-named
“acceptance interval” we reject H0 because its evident unlikeliness.
Thanks so much, Charles (you are a very special person, all we can state)
By the way: I would be really gratful for your corrections, indeed.
Luís
Done
Charles
This time
___pvalue less than alpha________significant________H0 rejected
___pvalue greater than alpha_____not significant_____fail to reject H0
Luís
Charles, please:
It would be feasible to eliminate my 1:37 am post?
Many thanks
Luis
Done
April 6, 23:30
Hi Charles
I had just read your introduction on NHST.
Excellent, you touch the main points, clearly , straightforward.
When we see so much trash in literature for example “accept the null”,
“the null is never attained, therefore the tests are useless”, and so on,
I am happy to read from you what is not seemly obvious to some scientists/professors
in particular Psychologists and Biologist as you surely had found. Well done Charles,
indeed.
Though we deliberated to retain 95% (say) probability to the Null Hypothesis
and a scarce 5% to the Alternative we are never apt to “accept” H0, not whithstand
found in a no few statistical literature. Jargon? could be, but dangerous
for beginners. On contrary In case the test falls outside ill-named
“acceptance interval” we reject H0 because its evident unlikeliness.
Luís
pleas explain to me this question my problem is this when I face to any question in hypotheses I can not Analyse how to make null and alternate hypotheses and about choosing the tailed, which tailed should I choose .pleas make me clear about this doubt .
thank you
Naqeebullah
Null/alternative hypothesis: The best thing to do is look at lots of examples and see how these hypotheses are defined. There are numerous examples given throughout the website. See, for example, the t test.
Tails: Generally you choose the two tailed test. Only when you are pretty sure (usually on theoretical grounds) that one of the tails won’t occur should you consider using a one-tailed test.
Charles
Hi Charles,
The terminology of type I /II errors seems a bit counter-intuitive. If a test result is wrong, then I would agree to call that a ‘false’ test result (i.e. wrong/error= false and accordingly, type I and type II are both called ‘false’). However, if the null hypothesis H0 is ‘rejected’ by the test, then I would call that a ‘negative’ test result (i.e. rejected = negative). Hence the type I error event that a true Ho is rejected, would be called a ‘false negative’
What is the alternative logic of calling a Type I error a ‘false positive ?
Hi Simon,
Here, the word positive is used since the null hypothesis is actually True. The word false is used since the conclusion is wrong, namely to reject the null hypothesis.
Charles
Hello Charles. Could you please give me directions how to solve such a question:
Test the null hypothesis that apples stock beta equals 1 using a two-tailed test. Make sure that you state the null and alternative hypotheses, the degrees of freedom used and the critical value from the Student’s t distribution.
Significance level: 5 %
coefficient: 1.28505377591414
Standard error: 0.0723764939179485
do i need to use a formula for calculating the hypothesis?
also the observations are 265
Alexander,
I don’t have enough information to provide a definitive answer, but it looks like you need to apply a two tailed t test, probably using the T.DIST formula.
Charles
If we perform a one tailed test and our directional prediction was incorrect, do we fail to reject the null?
I often see:
H0: u1 = u2
Ha: u1 > u2
So let’s say the test shows we were wrong, in fact u1 < u2. But u1 does not equal u2, so it's difficult for me to want to fail to reject the null. I just did a test like this and I want to reject the null although I was directionally wrong.
Is it the case that even though the null was written as (=), in actuality, there is a tacit agreement that we really mean (= OR <)? Because I really do see this often–the null being written only as (=) and not (= or ). I am having trouble finding a consensus on whether or not to reject the null when you chose the wrong direction. Thanks.
Kyle,
You only perform a one-tailed test if you are sure that one side of the test is impossible. For the example you gave, you are assuming that u1 < u2 can't happen. If you are not sure of this, then you should perform a two tailed test. Charles
plz answer this question
why we donot test alternate hypothesis in statistics
Generally we are more concerned about a type I type error than a type II type error.
Charles
Why we use null hypothesis in statistics instead of alternative hypnosis???
Maryam,
I believe that it is for historical reasons, but in any case the null and alternative hypotheses are flip sides of the same coin.
Charles
Question
if there is alternate hypothesis then why we use null hypothesis in statistics? kindly explain briefly
Raza,
It is very common that you are trying to refute the null hypothesis in order to show that alternative hypothesis is true. Recall that the alternative hypothesis is true if and only if the null hypothesis is false.
Charles
i see . .! but why we try to reject or accept null hypothesis in ordered to prove alternate hypothesis accepted or rejected , , why not we directly proved or disproved alternate hypothesis . . .? little bit confusing this , , kindly guide it
Our teacher asked this question to us and I really need to know the answer so if you can be of help, please do.
“What is the main characteristic of the null and alternative hypothesis?”
It’s only 1 main characteristic.
I am afraid that you will need to provide this answer yourself, but hopefully the referenced website helps you with the response.
Charles
I see. Thank you. It did help but I did have a bit of a trouble picking the best characteristic to pick based on what you wrote in the article.
i still cant understand about the alternative hypothesis. help?? please.
Christine,
To give a silly example, if the null hypothesis is “all dogs are aggressive” then the alternative hypothesis is the opposite, namely “not all dogs are aggressive”. Often you expect the alternative hypothesis to be true. If you need more help, please be more specific about the sort of help you need.
Charles
in hypothesis testing, I assume that the null hypothesis is true in the sample or the population?
Jenny,
The null hypothesis is about the population.
Charles
Question:
Did students prefer to skip class the day before spring break , or the day after spring break ?
John has reviewed about 200 fellow students selected at random in the University. He found that there were 120 students prefer to skip class the day before spring break , and 80 students were chosen to skip classes a day after spring break. Fifty of these individuals also have chosen to skip two days of spring break.
What is the hypothesis null & alternative? How to calculate the P-Value manually?
Terence, sorry but I don’t understand the relevance of the 50 students who skipped two days of spring break. Also are these 50 of the 200 students or 50 of the 80 students?
Ignoring the 50 students, this seems to be a problem regarding the binomial distribution. I suggest that you look at hypothesis testing for the binomial distribution. See webpage Hypothesis Testing for the Binomial Distribution.
Charles
Thanks Dr. Charles.
Your notes were quite helpful to me but I have a worry,what in a case where there was statistical significance with a chi-square test n for the same variable,no significance with a logistic regression model, what then should the conclusions on the hypothesis be based on?
Aki,
I would have to see the specific results to answer precisely, but, in general, it can happen that you run two different statistical tests and get different, even contradictory, results. Sometimes this is because some assumption has not been met in one of the tests. Sometimes it is because the results are similar but the conclusions are different (e.g. the p-value for one test is .051 and the p-value for the other is .049). Sometimes one test is more accurate (e.g. the t test when the assumptions are met vs. a non-parametric test such as Mann-Whitney).
In any case, this is the nature of statistical testing: it is probabilistic in nature. When this happens, you should report both results and draw whatever conclusions make sense, even that no clear-cut conclusion can be made.
Charles
Hi Thomas,
I need some guidance here.
I’m using f-test to check for the equality of variance between two sample of mean score of multifactor leadership questionnaire before deciding which t-test to perform. The p-value of each nine dimensions gave me mix of significant where three out of nine are greater than 0.05 and the rest are lower than 0.05. In this situation, can I conclude that the variance is not equal since majority fall within less than .05?
Thanks for your help.
Regards,
ST
Hi Charles,
Sorry, I have mistakenly address you wrongly.
Please accept my apologies..
Regards,
ST
ST,
I don’t completely understand the scenario, but it is very unlikely that it would be correct to conclude that the variances are not equal simply because the majority are less than .05.
Charles
Thanks Charles, I’m collecting data for two random samples using the questionnaire I mentioned earlier. In this questionnaire, there are nine dimensions each representing different leadership style. I’ve applied the f-test on each dimension to check for the equality of variances and below is what I got.
Dimension F Significant
IIA 1.9215 0.0392
IIB 1.9215 0.0175
IM 1.6443 0.0535
IS 2.1763 0.0062
IC 1.9863 0.0135
CR 1.1428 0.0016
MBEA 1.1428 0.3331
MBEP 1.5012 0.0936
LF 2.1530 0.0068
From the significant value obtained, there are three dimensions having more than 0.05. That’s why I’m struggling to make the conclusion whether these two samples are having equal or unequal variances. Meanwhile, I have also computed the t-test two-sample equal and unequal variances, all dimensions except one (MBEA) are significantly below 0.05.
I understand from your earlier feedback that it is likely that I could conclude the variances are not equal and I guess I’m not able to conclude to equal variances either. In this instances, do you have any other recommendation that I could use or test to analyse the two sample data? My objective of this study is to find out whether there is any differences between these two samples.
Hope you could be in help. Thanks for your time.
Regards,
ST
ST,
What I said previously is that even if the variances are equal the t test with unequal variances should be pretty accurate. Since the p-value > .05 for the t test for MBEA, then you cannot reject the hypothesis that the (population) means for MBEA are equal. Since the p-values for the other tests are less than .05, you conclude with 95% confidence that the means for these dimensions are equal.
The only problem with this approach is that 9 tests, and so you have introduced an experiment-wise error of more than 5%. You might want to use a corrected alpha value as described on the webpage
https://real-statistics.com/one-way-analysis-of-variance-anova/experiment-wise-error-rate/
Charles
Dear Charles,
I am working on my final master’s paper and have to do some t-tests.
The idea is to test whether certain groups of people, classified with a self-reported score, the Need for Cognition, that helps to identify people as those who like intellectual tasks and to think problems through and those who don’t are more likely to answer another set of questions consistently with the same answer or whether they change their answer depending on how the question is asked and presented.
I am not sure how to formulate my null hypothesis here. I expect those with a high Need for Cognition score to answer questions more consistently and not to be affected by how the objectively equivalent messages are framed/presented.
Can you help me with the hypothesis formulation and then the decision which t-test (one-sided vs. two-sided) to choose?
Thank you very much in advance!
Best regards,
Thomas
Thomas,
I would need to see more details to answer your question definitively, but I can think of two possible approaches.
(1) Null hypothesis: The mean score for the two group are the same. When in double, use a two tailed test. When you are pretty sure that mean score for group 1 can’t be less than the mean score for group 2, then you could use a one-tailed test.
(2) Don’t view this problem as one of hypothesis testing of means, but as a comparison of ratings and use Cohen’s kappa or something similar.
Probably the approach you are looking for is approach (1).
Charles
Thank you Charles!
I think the two-tailed test for an equal mean score is the correct thing here.
I used a hypothesized mean difference of zero, which should be the right test, correct? This means, I test if the mean difference between those two groups (high NFC versus low NFC group) is equal to zero, and if it is close enough to zero , the test result would tell me there is no mean difference. This would mean, people answer equally consistent no matter to which group they belong?
My two-tailed critical value is 1.97 and the t-Stat is -2.02. Somewhere I read, if the t-Stat (-2.02) is below the negative critical value (-1.97), which is the case in my study, I shall reject the null hypothesis. Is this correct, too?
In my case, then, the hypothesized mean difference of zero should be rejected, i.e. the two groups actually have a mean difference of larger than zero, hence the two groups performed differently consistently.
Thanks again!
Thomas
I have two samples from a batch of paint. One sample is taken from the manufacturer and another sample is taken from the same batch when sent to the applicator’s yard. The testing agency is the same for each test. What I am trying to show is that their is no significant difference in testing results taken from these separate locations. Is a paired t test the appropriate approach?
Since you can’t look at each of the sample elements as paired in any way, the paired t test doesn’t seem appropriate. I guess that I would use a two sample t test (provided the normality assumption is met), although strictly speaking the samples are not completely independent.
Charles
Hi there,
I having a lot of trouble with determining the p value. How do i find it with a sample size of 124 and a alpha level of 0.5. Also what test would i use to test the null hypothesis with the two nominated variables of stress levels and perceived stress levels (have to see if they are related). Also how do i state the assumptions for the test?
Thanks kindly,
Madison
Sorry also, step three above, how do i know which test to run?
Madison,
The referenced webpage is only intended to explain the general approach to hypothesis testing. The actual approach used depends on the specific hypothesis that you are trying to test. Much of the rest of the website addresses the various types of hypothesis testing that you might need to do.
Regarding your specific problem, it sounds like you are trying to see whether there is a correlation between perceived and measured stress. This is likely to be addressed using a t test (or an equivalent correlation test). See the following webpages for more details:
Paired Samples t Test
One Sample Hypothesis Testing for Correlation.
Also, it unlikely that you want an alpha of .5. You probably mean .05.
Charles
Given the following information… how do you extract the null hypothesis equation? Thanks
A study was designed to compare three different methods for reducing stress. Sixty employees in a corporation were randomly assigned to each of the following groups for a two-week period: exercise, relaxation training, and management skills training (learning to set priorities, communicate effectively, resolve conflicts). Data consisted of subject scores on a measure of stress in the workplace taken after each two-week training period.
This is very helpful but I’m still not sure how to calculate the power of my equation and how to calculate the probability of a Type II error.
Cynthia,
This depends on the “equation” that you are using.
Charles
I have a simple regression equation and want to calculate the power and probability of a type II error. Many thanks
Cynthia,
Please look at the following webpage
Power for Multiple Regression
Charles
Thanks!
please, I need your assistance to answer this question. State ten null hypotheses and ten alternative hypotheses for me.
Cletus,
Sorry, but I don’t understand the question.
Charles
Hi Charles,
Please I need assistance to answer this question.
In the test of difference and relationship, explain how to reject a null hypothesis and as well as accepting an alternative hypothesis.
Joy,
This is explained on the reference webpage. In general you set up a statistical test and calculate a p-value. If the p-value < alpha then you reject the null hypothesis. If something on the webpage is not clear to you, please ask a more detailed question about that concept. Charles
Please I need assistance in my research work in data analysis and presentations. I have 3 objective as thus: what are the problems teachers are facing in teaching English in secondary school. What are the problems learners face in learning English. What are the solutions to the problems of teaching and learning English language in sec school. Then my hypothesis is there is no significant difference between the problems identified as affecting the teaching of English language and that of learning it in sec school in PH LGA. Please am using frequency count and percentage methods of data analysis. I need more explanation on it and how to calculate the hypothesis.
Thanx
Pamela,
I am sorry, but the information you have provided is not specific enough for me to offer any advice.
Charles
Hello Sir,
i wanted to know that how is “non central distribution” used in the testing of hypothesis?
Vicky,
The non-central distributions are used to calculate beta or power. The details are shown in various places on the website. E.g.
https://real-statistics.com/students-t-distribution/statistical-power-of-the-t-tests/
Charles
I have this problem in a class and am in desire need of help. Thanks
Share with your peers the null and alternative hypotheses for a decision that is relevant to your life. This can be a personal item or something at work. Additionally, identify the Type I and Type II errors that could occur with your decision‐making process.
Machelle,
It is not possible for me to create hypotheses for your life. Just come up with something similar to the various null/alternative hypotheses that you see throughout the website.
Charles
i have a critical question concerning above issue. can we say that we have two constructs of hypothesis namely , alternative,null hypothesis? the former is more abstract than null. i mean that the researcher should firstly maintain or reject null to touch abstract construct that’s to say,alternative research.put differently,alternative hypothesis is grounded on null- hypothesis. am i right?.i look forward to hearing from you
I am not sure that I follow you completely, but I think that in some sense you are correct. Usually (although not always) you posit the null hypothesis with the goal of proving the complement, namely the alternative hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis is completely determined by the null hypothesis, namely the alternative hypothesis is true if and only if the null hypothesis is false. If you look at some older statistics text books, this wasn’t exactly the way it was stated, and may have been more aligned with your approach. In any case, today they are simply complements of each other and so if you think of the null hypothesis as concrete then the alternative hypothesis is just as concrete.
Charles
May I get some assistance on a QMB class by using Microsoft Excel.
Best regards,
Anorve Belizaire
Anorve,
If by QMB you mean quantitative methods in business, then the answer is yes.
Charles
Dear Charles,
at the end of the article, is seems that a small error is still present :
“The general procedure for null hypothesis testing is as follows:
State the null and alternative hypotheses
Specify and the sample size”
Maybe the “and” should be removed ?
Thanks again for you wonderful website (and for your yesterday’s answer),
Gilles
Dear Gilles,
It should say “Specify alpha and the sample size”. I have now made this correction on the referenced webpage. Thanks for catching this typing omission. I am pleased that you are enjoying the website and making valuable contributions as well.
Charles
Thanks a lot for this site! I’m a psychologist from Brazil and I’m doing a study here that requires statistical analisys, and you’re helping me alot!
Thanks again! Your site is the best one for learning how to use excel for statistical work!
Hi. I’m doins a research on motivation and de-motivation among students. I’m using 3 independent variables. I’m testing how the 3 IV affect motivation and de-motivation. Should I use null hypotheses to test motivation and de-motivation? At the same time I’m using 2 dependent variables(motivation and de-motivation).
Would appreciate your help. tq
Dee,
Sorry, but I need more information about what you are trying to accomplish before I am able to answer your question.
Charles