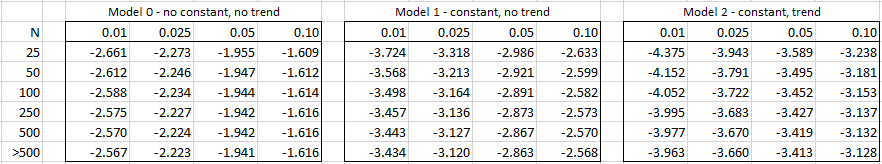
If the calculated tau value is less than the critical value in the table above, then we have a significant result; otherwise, we accept the null hypothesis that there is a unit root and the time series is not stationary.
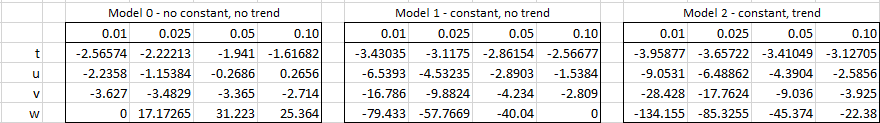
The following is a more precise way of estimating these critical values:
crit = t + u/N + v/N2 + w/N3
where t, u, v, and w are defined as follows:
See Dickey-Fuller Test and Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test for more details.
Download Table
Click here to download the Excel workbook with the above table.
References
Dickey, D. A., Fuller, W A. (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with unit root. Journal of the American Statistical Association. Vol 74.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/243644934_Distribution_of_the_Estimators_for_Autoregressive_Time_Series_With_a_Unit_Root
Wikipedia (2016) Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Augmented_Dickey%E2%80%93Fuller_test
Minitab (2016) Methods and formulas for Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
https://support.minitab.com/en-us/minitab/help-and-how-to/statistical-modeling/time-series/how-to/augmented-dickey-fuller-test/methods-and-formulas/methods-and-formulas/
Fuller, W. A. (1976). Introduction to statistical time series. New York, Wiley.
MacKinnon, J. G. (1994). Approximate asymptotic distribution functions for unit-root and cointegration tests. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 12, 167-176.
https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/273255?v=pdf
MacKinnon, J. G. (2010). Critical values for cointegration tests: Working paper 1227. Queen’s University, Department of Economics.
https://www.econ.queensu.ca/sites/econ.queensu.ca/files/wpaper/qed_wp_1227.pdf
Tamer, K. (2014) Lag order and critical values of the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test: a replication
https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/60456/1/MPRA_paper_60456.pdf
Hello Charles:
I have been following your page with keen interest, and I like the fruitful discussions. Thanks for adding real value to enrich our knowledge base.
How do to proceed to use the ADF to test for the unit root fror a set of variables simultaneously, and which table of tables should i consult for the relevant critical tables? Thanks.
Samuel
Hello Samuel,
I am not familiar with a specific ADF test for a set of variables. You could perform separate ADF tests for each variable and use a Bonferroni correction to account for the multiple tests, but I don’t know whether is the best approach.
Charles
In order to find which ADF model to choose, can we apply OLS regression on variable with constant and time trend? If not, why?
Hello Muhammad,
That probably will do the job. You can also create a graph of your data.
Charles
Dear Charles,
Thank you for your excellent presentation of Dickey-Fuller tests as well as the Augmented Dickey Fuller tests.
I am however confused about the Augmented Dickey-Fuller Table of Critical Values. First, the table differs from the one in Fuller’s book (1996, Appendix A). Second, I could not find the formula:
t + u/N + v/N2 + w/N3
and the tables where t, u, v, w are defined in the reference you gave in your reply to Lee’s question.
Could you please clarify?
Thank you in advance.
Best regards,
Alberto
Do you know how/where can I get right-tailed critical values of the asymptotic distribution of the Dickey–Fuller statistic to test for the alternative of explosive root?
Thanks in advance.
Hello Marcio,
I found this table:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324086519_Date-stamping_US_housing_market_explosivity/figures?lo=1
The following is also probably useful:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1873871
Charles
Hey There,
The Dickey-Fuller critical values are -2.57 at the 0.10 level, -2.86at the 0.05 level, and -3.43 at the 0.01 level. For each variable, what would you conclude about the presence of a unit root?
Hi Jane,
See https://www.real-statistics.com/time-series-analysis/autoregressive-processes/augmented-dickey-fuller-test/
Charles
Dear Charles,
may I ask where the formula for critical value calculation comes from? Could you please mention the source?
Thank you!
Hi Lee,
Distribution of the Estimators for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root
David A. Dickey & Wayne A. Fuller
Pages 427-431 | Received 01 Nov 1976, Published online: 05 Apr 2012
Charles
Dear Charles,
if the time series is not stationary with a constant and is stationary with a constant and a trend, do I need to difference the time series or can assume stationarity for the model with a constant and a trend and go on with further calculations? I’m not sure how to estimate whether there is a trend in general or not. Can I measure a trend with R-squared?
Kinds regards
Agata
Hello Agata,
The easiest way to spot a trend is to look at a graph of the time-series data.
See https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-a-trend-in-time-series/
I don’t know any way of using R-squared to spot a trend.
Charles
Hye Charles.
I have a question.
Due to the limited no of sample size in the table.
Lets say the sample size is 37, so we have to look at the approximate, n= 50 or 25?
Is there any table contains large options on sample size?
Thanks Charles.
Hi Nabilah,
You can interpolate between the 25 and 50 values in the table. 37 is about halfway between these values.
If you have the Real Statistics software installed, you could use the ADFTEST function.
Charles
Dear Charles, congrats for this post. I havia a question, what is the meaning Model 0, 1 and 2 ?
Regards
Henrique
What is “no constant” ?
No intercept.
See my response to your other comment.
Charles
Dear Henrique,
See the following two webpages:
https://www.real-statistics.com/time-series-analysis/stochastic-processes/dickey-fuller-test/
https://www.real-statistics.com/time-series-analysis/autoregressive-processes/augmented-dickey-fuller-test/
Charles
Dear Charles
Should we compare both of them (p-value with alpha and Observed value with Critical value) for stationary test in ADF test as the following down?
Tau (Observed value) -3.7271
Tau (Critical value) 0.9768
p-value (one-tailed) 0.1991
alpha 0.05
Test interpretation:
H0: There is a unit root for the series.
Ha: There is no unit root for the series. The series is stationary.
You only need to use one of them (p-value or critical value). They should give the same answer.
Charles
There are three ways to deal with the problem of model choice.
1. You may have a look at the graph.
But the problem is that if the graph shows an intercept or drift it may not be statistically significant and hence is treated as zero. Similar is the case with slope of the trend line.
2. Try out all three models in e-views or any other software and compare the r -square. The one with the highest r-square is the best.
3. Best is to estimate the full model with drift and trend and examine whether intercept and/ or slope is statistically significant at 5% level and then infer the correct model.
Prof. K. V. Bhanu Murthy
Thank you for your insights about this issue.
Charles
Dear professor
I would like to connect to you, for learning this
Dear Sir,
This was a helpful explanation , much appreciated.
However I have a little confusion.
The results of ADF
t- statistic -7.335489
p-value 0.0000
Test critical values: 1% -4.374307
5%. -3.603202
10% -3.238054
The variable tested does not contain a unit root, thats clear to me. But I want to know if it is significant at 1% 5% 10% or all three? If it is significant on all three then which one should be reported in the output table?
Thanks in anticipation
Ayesha
Ayesha,
If p-value = .0000 then significance is at far less than 1% (even less than .001%).
Charles
your assumption on critical value is false and misleading. better check out sir. it will confusing others. to make it significant, calculated t-value should exceed the Augmented Dickey Fuller or Phillips Perron stats!!!!!
The null hypothesis is that there is a unit root. You reject the null hypothesis when the calculated statistic is less than the critical value, in which case you have evidence that the time series in stationary. Since the critical values are negative numbers, less than is equivalent to greater than when you take the negative of the calculated value and critical value.
Charles
Dear Charles,
How to choose right ADF table when to look up t statistic? Model 0 or Model 1 or Model 2? This is a little bit complicated for me and I highly appreciate your interpretation.
Steven
Hello Steven,
I suggest that you create a chart of the data and see whether there is a trend or intercept.
Charles
Muito instrutivo teu site
Tenho uma dūvid a quanto a qual tabela usar
Sem constante sem tendência com tendência
Como posso automatizar isso?
Hello Felipe,
Glad that you get value from the website.
You need to look at the data to determine which table to use (e.g. do you see a trend in the data?)
Charles
Dear Charles,
Will you please tell me the source from where you got the critical values to test the stationary.
Hello.
See the Evans and Stanford University entries in the Bibliography at
Bibliography
Charles
Dear Charles, Thanks for the explanation here. I however have a query.
Is it possible to confirm which of the three models (no constant no trend//constant no trend//with constant and trend) is applicable for any timeseries just by looking at the output Tau Statistics and the associated pValues?
If not, then is there any statistical way to identify which model to be used?
Hello Zafar,
I suggest that you graph the data to see whether there is a trend and whether there the mean is zero.
Charles
According to given above statement(If the calculated tau value is less than the critical value in the table above………,) is presents. but in using Xlstate the assumption is raised if the P value is less than the significant level the series is stationarity
Dickey-Fuller test (ADF(stationary) / k: 2 / Series1):
Tau (Observed value) -3.7271
Tau (Critical value) 0.9768
p-value (one-tailed) 0.1991
alpha 0.05
Test interpretation:
H0: There is a unit root for the series.
Ha: There is no unit root for the series. The series is stationary.
As the computed p-value is greater than the significance level alpha=0.05, one cannot reject the null hypothesis H0.
The risk to reject the null hypothesis H0 while it is true is 19.91%.
By using of Xlstat above results shows non-stationarity why? please guide me. furthermore, any test is available for contingency table.
Kind Regards
Muhammad Fahim Akhter
Hello Muhammad,
Since the null hypothesis is that the series is non-stationary and p-value = 0.1991 > .05, you can’t reject the null hypothesis and so you should conclude that it is likely that the series is non-stationary.
Charles