In Logistic Regression Sample Size (Normal) we describe how to calculate the minimum sample size for logistic regression when the main independent variable being studied is normally distributed.
Binary Distribution Case
We now describe the case where the independent variable has a binomial distribution. In this case, the minimum sample size is
where π = portion of the sample where x = 1 and
p0 = P(y = 1|x = 0) p1 = P(y = 1|x = 1)
We use the same correction as described in Logistic Regression Sample Size (Normal) when there is more than one independent variable, namely
Note that if we know p0 and OR, we can solve for p1 as follows
![]()
![]()
![]()

Example
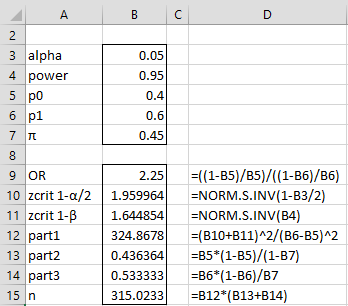
Example 1: A study is being organized to determine whether men or women are more likely to be prescribed opioids for pain. Here x = gender (0 = female and 1 = male) and y = prescribed opioids for pain (1 = yes, 0 = no). We assume that 45% of the people in our sample will be men and that 40% of the women will get a prescription while 60% of the men will get a prescription. We want to determine how big a sample we need to conduct this study (further assuming a 95% significance level and 95% power).
As we can see from Figure 1, the minimum sample size is 316.
Figure 1 – Sample size binary independent variable
Examples Workbook
Click here to download the Excel workbook with the examples described on this webpage.
References
Hsieh, F. Y., Bloch, D. A., Larsen, M. D. (1998) A simple method of sample size calculation for linear and logistic regression. Statistics in Medicine
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9699234/
Buchner, A., Erdfelder, E., Faul, F., Lang, A-G (2021) G*Power 3.1 manual
https://www.psychologie.hhu.de/fileadmin/redaktion/Fakultaeten/Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche_Fakultaet/Psychologie/AAP/gpower/GPowerManual.pdf
Hsieh, F. Y. (1989). Sample size tables for logistic regression. Statistics in medicine, 8, 795-802.
http://www.statpower.net/Content/312/Handout/Hsieh%281989%29.pdf
Would this be the same method that G*Power employs to calculate the sample size for binary logistic regression with a binary independent variable?
Hello Ana,
I had thought that I had used the same approach as G*Power, but apparently not. For the example on the webpage n = 316, while G*Power calculates a sample size of 328. I need to check whether I made some error or the approach was a little different.
Charles
Ana,
I just checked G*Power and confirm that the approach that I am using is different from that used by G*Power. The results should be similar but not the same.
Charles
Please explain how you got the P0 and P1 values in Figure 1?
Hello Olivia,
The P0 and P1 values shown in the figure are incorrect. I have now corrected this.
Thank you for identifying this error. I appreciate your help in improving the quality of the Real Statistics website.
Charles