Essentially, RCBD (without replications), as described in Randomized Complete Block Design is equivalent to two-factor ANOVA without replication where the rows are the block factor and the columns are the treatment factor. In a similar manner, RCBD with replication is equivalent to two-factor ANOVA with replication.
Example
Example 1: An agronomist wants to compare the yields of three varieties of cotton. The land is divided into four rectangular fields (the blocks). Field 1 is located near a river and field 4 is near a road. The other two fields are between them. The confounding factors (soil quality, water, etc.) are fairly uniform within a field, although they may be different among the fields. Each field is divided into 6 plots. Each variety is randomly applied to two plots in each block as shown in Figure 1, which also shows the yield from each plot.
Determine whether the cotton variety affects yield and whether there is an interaction between field and variety.
Figure 1 – Plot layout and yield
Using ANOVA
The data can be reformatted for use by the Two Factor ANOVA with Replications data analysis tool, as shown on the left side of Figure 2.
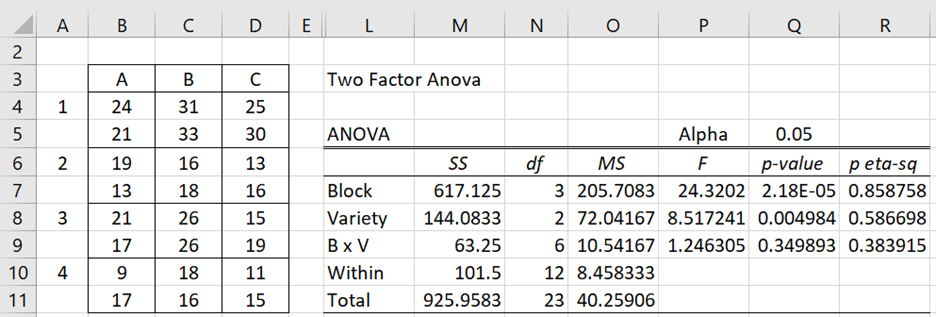
Figure 2 – ANOVA design
The results from the Two Factor ANOVA with Replications data analysis tool are shown on the right side of Figure 2 where Rows has been replaced by Block and Columns by Variety. We see that the cotton variety affects yield, i.e. there is a significant difference between the 4 treatments (p-value = .005), but there isn’t an interaction between field and variety (p-value = .35).
Examples Workbook
Click here to download the Excel workbook with the examples described on this webpage.
References
Montgomery, D. C. (2012) Design and analysis of experiments. 8th ed. Wiley
https://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/sites/default/files/douglas_c._montgomery-design_and_analysis_of_experiments-wiley_2012_edition_8.pdf